Burp MCP + Codex CLI
-
This guide shows how to connect Burp Suite MCP Server to Codex CLI so that Codex can reason directly on your real HTTP traffic — no API keys, no scanning, no fuzzing.
-
You end up with a reasoning engine wired directly into your interception stack.
What you get
-
Passive vuln discovery
-
IDOR / auth bypass / SSRF / logic flaw detection
-
Report writing from real Burp evidence
-
No API keys
-
Full local traffic control
Installation
1. Install Burp MCP Server
- Install MCP Server from Burp’s BApp Store.
Once installed, open its tab and click Exctract server proxy jar
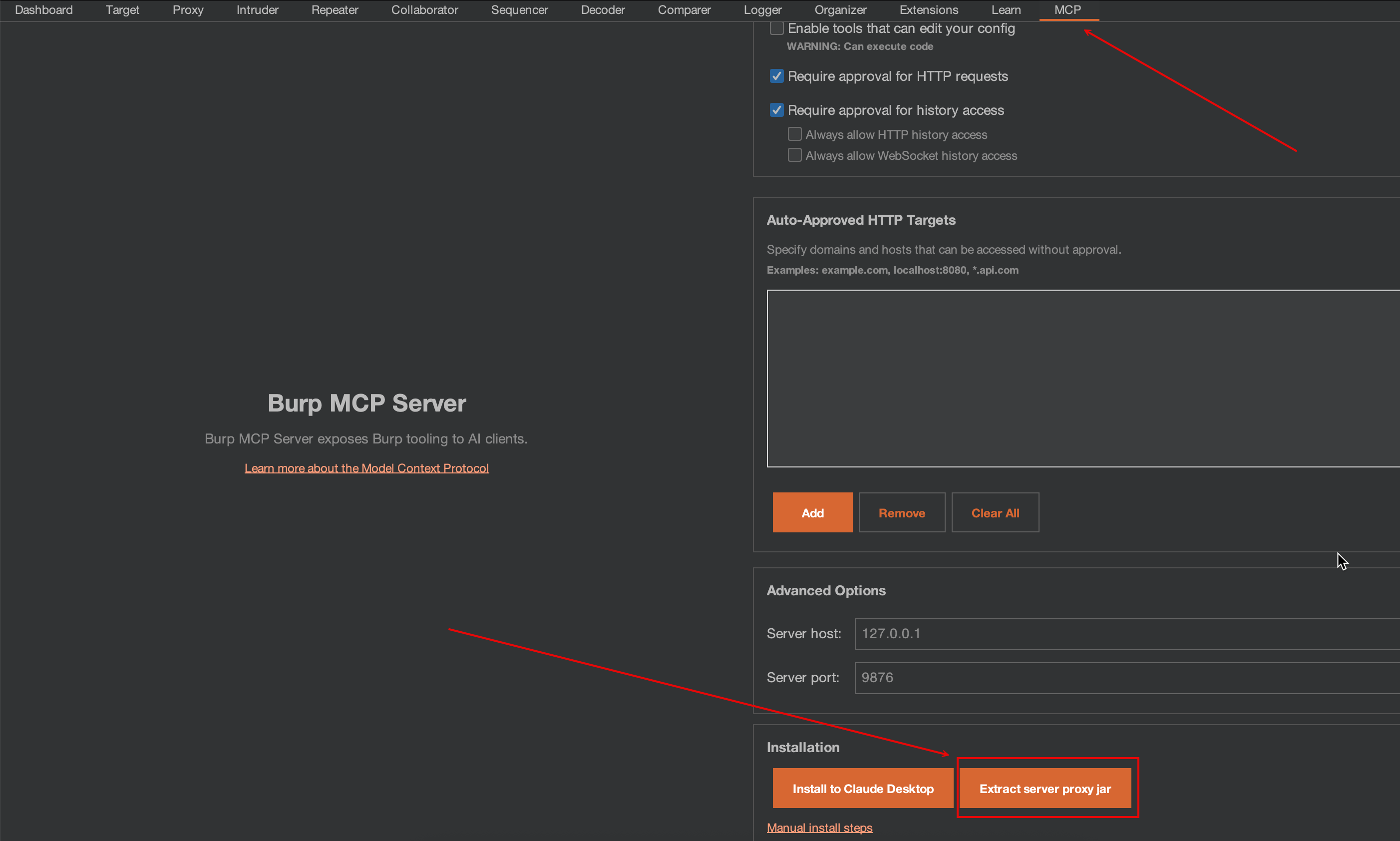
- This then downloads
mcp-proxy.jar
2. Configure Codex MCP
-
Go to ~/.codex.config.toml and edit that
-
Add this:
[mcp_servers.burp]
command = "java"
args = ["-jar", "/absolute/path/to/mcp-proxy.jar", "--sse-url", "http://127.0.0.1:19876"]- Make sure you remember to change the path!
3. Install Caddy reverse proxy
-
Burp MCP currently enforces strict
Origin validationand rejects extra headers sent by Codex, which causes handshake failures see more here. -
We solve this with a local reverse proxy.
3. Install Caddy:
brew install caddy4. Create the Caddyfile
Create with nvim or nano
~/burp-mcp/CaddyfilePaste this into the file:
:19876 {
reverse_proxy 127.0.0.1:9876 {
header_up Host "127.0.0.1:9876"
header_up Origin "http://127.0.0.1:9876"
header_up -User-Agent
header_up -Accept
header_up -Accept-Encoding
header_up -Connection
header_up -Referer
header_up -Sec-Fetch-Site
header_up -Sec-Fetch-Mode
header_up -Sec-Fetch-Dest
}
}5. Start everything up
caddy run --config ~/burp-mcp/Caddyfile &
codex6. Verify
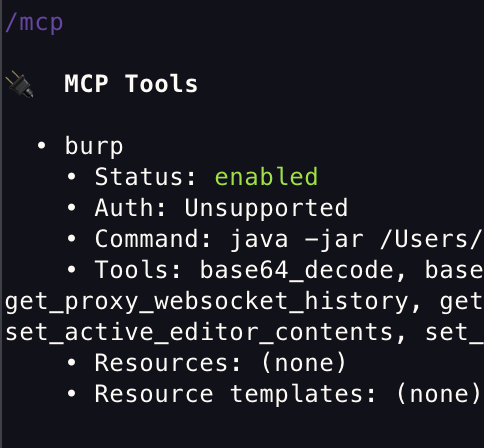
- When inside of codex type in
/mcp
You should receive this:
7. Test it out
- You can use those examples:
From Burp history, find all endpoints that use numeric IDs and lack Authorization headers.Using Burp MCP, identify potential IDOR endpoints and suggest safe confirmation steps.From Burp data, write a vulnerability report with reproduction, impact and remediation.8. One-command launcher (optional)
- Add to your ~/.zshrc (check your paths first):
burpcodex() {
emulate -L zsh
setopt pipefail
local CADDYFILE="$HOME/burp-mcp/Caddyfile"
local LOG="/tmp/burp-mcp-caddy.log"
local CADDY_PID=""
if ! command -v caddy >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "[!] caddy not found (brew install caddy)"
return 1
fi
if ! command -v codex >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "[!] codex not found in PATH"
return 1
fi
if [[ ! -f "$CADDYFILE" ]]; then
echo "[!] Caddyfile not found: $CADDYFILE"
return 1
fi
cleanup() {
# 1) Kill captured PID (if still alive)
if [[ -n "$CADDY_PID" ]] && kill -0 "$CADDY_PID" 2>/dev/null; then
kill -TERM "$CADDY_PID" 2>/dev/null
sleep 0.2
kill -KILL "$CADDY_PID" 2>/dev/null
wait "$CADDY_PID" 2>/dev/null
fi
# 2) Fallback: kill anything still listening on 19876
local pids
pids="$(lsof -ti tcp:19876 2>/dev/null | tr '\n' ' ')"
if [[ -n "$pids" ]]; then
kill -TERM $pids 2>/dev/null
sleep 0.2
kill -KILL $pids 2>/dev/null
fi
}
trap 'cleanup; return 130' INT TERM
trap 'cleanup' EXIT
# Start caddy
caddy run --config "$CADDYFILE" >"$LOG" 2>&1 &
CADDY_PID=$!
echo "[*] Caddy started (pid=$CADDY_PID) - log: $LOG"
# Run codex (foreground)
command codex "$@"
# Ensure cleanup even if trap didn't trigger for some reason
cleanup
trap - INT TERM EXIT
}9. Tips and troublshooting
- If Render Page crash:
sudo sysctl -w kernel.unprivileged_userns_clone=1
- If embedded browser crash due sandbox:
find .BurpSuite -name chrome-sandbox -exec chown root:root {} \; -exec chmod 4755 {} \;
- Scope with all subdomains:
.*\.test\.com$
-
Use Intruder to target specific parameters for scanning
- Right click: actively scan defined insertion points
-
Configuration
- Project Options → HTTP → Redirections → Enable JavaScript-driven
- User Options → Misc → Proxy Interception → Always disabled
- Target → Site Map → Show all && Show only in-scope items
-
XSS Validator extension
- Start xss.js phantomjs $HOME/.BurpSuite/bapps/xss.js
- Send Request to Intruder
- Mark Position
- Import xss-payload-list from $Tools into xssValidator
- Change Payload Type to Extension Generated
- Change Payload Process to Invoke-Burp Extension - XSS Validator
- Add Grep-Match rule as per XSS Validator
- Start
-
Filter the noise
https://gist.github.com/vsec7/d5518a432b70714bedad79e4963ff320
-
Filter the noise TLDR
-
TLS Pass Through
- .*.google.com
- .*.gstatic.com
- .*.googleapis.com
- .*.pki.goog
- .*.mozilla.com
-
Send swagger to burp
https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/Swagger-EZ
- Hosted:
https://rhinosecuritylabs.github.io/Swagger-EZ/
-
If some request/response breaks or slow down Burp
- Project options → HTTP → Streaming responses → Add url and uncheck “Store streaming responses…”
-
Burp Extension rotate IP yo avoid IP restrictions
https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/IPRotate_Burp_Extension
-
Collab/SSRF/pingback alternative interactsh.com ceye.io requestcatcher.com canarytokens.org webhook.site ngrok.com pingb.in swin.es requestbin.net ssrftest.com rbnd.gl0.eu dnslog.cn beeceptor.com
-
Run private collaborator instance in AWS
https://github.com/Leoid/AWSBurpCollaborator
- Run your own collab server
https://github.com/yeswehack/pwn-machine
-
Wordlist from burp project file
cat project.burp | strings | tok | sort -u > custom_wordlist.txt -
Autorize:
- Copy cookies from low priv user and paste in Autorize
- Set filters (scope, regex)
- Set Autorize ON
- Navigate as high priv user
-
Turbo Intruder
basic.py→ Set %s in the injection point and specify wordlist in scriptmultipleParameters.py→ Set %s in all the injection points and specify the wordlists in script -
Match and Replace
https://github.com/daffainfo/match-replace-burp
- Customize Audit Scans
Configure your audit profile → Issues reported → Individual issues → right-click on “Extension generated issues” → “Edit detection methods”
-
Works on most of issues like SQLi
-
Send to local Burp from VPS
- In local computer
ssh -R 8080:127.0.0.1:8080 root@VPS_IP -f -N - In VPS
curl URL -x http://127.0.0.1:8080
- In local computer
-
Ip rotation `https://github.com/ustayready/fireprox